TAP THE ICON to learn more about the type of infection
SEPSIS
(presence of bacteria in the bloodstream)
A life-threatening condition
Symptoms:
- Fever
- Chills
- Confusion or altered mental status
Complications:
- Limb amputation
- 1 in 8 adults with pneumococcal sepsis dies from the infection
MENINGITIS
(infection of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord)
Symptoms:
- Stiff neck
- Fever and headache
- Sensitivity to light
- Confusion or altered consciousness
- Vomiting, poor appetite
- Fatigue
Complications:
- 1 in 6 adults with pneumococcal meningitis dies from the infection
- High risk of neurological impairment or hearing loss after recovery
INVASIVE PNEUMONIA
(lung infection with bacteria present in the blood)
Symptoms:10
- Fever
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Productive sputum
- Pleuritic chest pain
Complications:11
- 30-day mortality is significantly higher in patients with bacteremic pneumonia (28.6%) compared to non-bacteremic cases (8.5%)
- Infection-related mortality is also higher in bacteremic pneumonia (19.5%) vs. non-bacteremic (4%)
ECONOMIC BURDEN

due to pneumococcal pneumonia occur each year in the United States.5

was spent annually on the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in the United States. (1996-1998).6

higher: The healthcare costs for high-risk individuals with pneumonia compared to healthy individuals.7
Your child may be at increased risk.

Your may be at increased risk

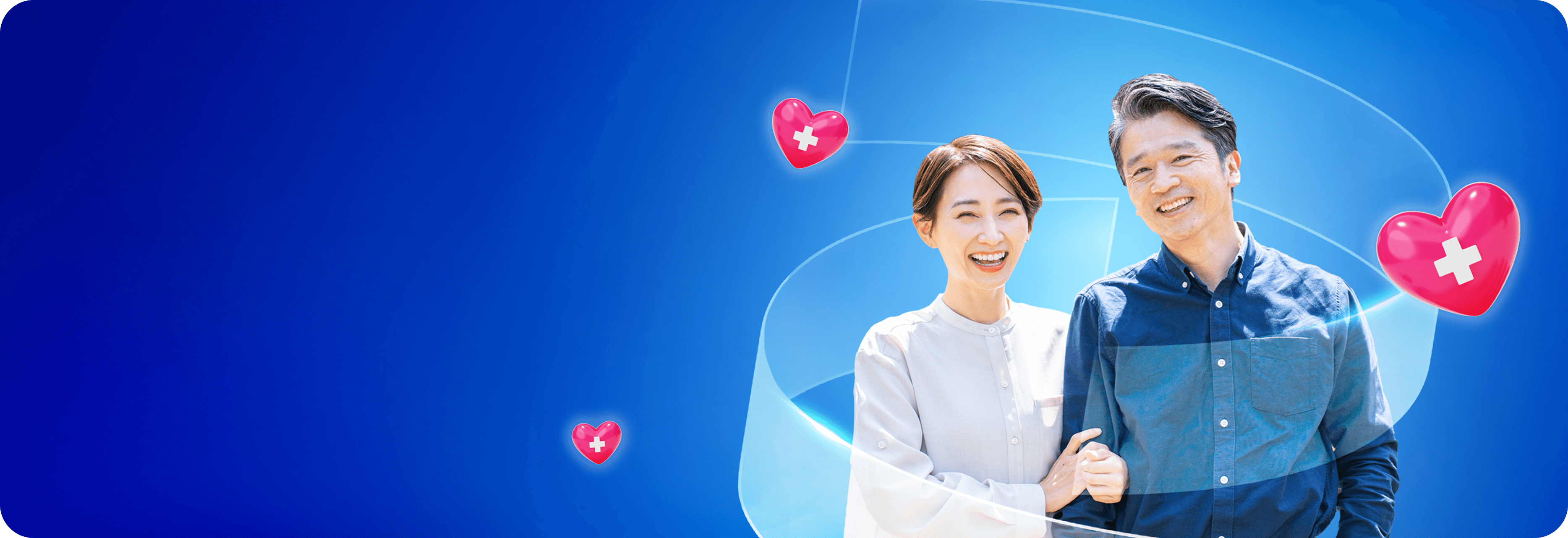
Worth your attention.Pneumococcus can lead to life-threatening diseases


What is Invasive Pneumococcal Disease (IPD)?
Invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) is a serious infection caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae when the bacteria invade normally sterile areas of the body, such as the bloodstream or the central nervous system. IPD includes conditions such as meningitis, sepsis (bacteremia), and invasive pneumonia. 2
How is pneumococcal disease transmitted?
Pneumococcal disease spreads through direct contact with respiratory secretions, such as saliva or mucus. Children who are not vaccinated are at higher risk of infection, partly because their immune systems are not yet fully developed. 2
What are pneumococcal serotypes?
Pneumococcal serotypes are classified based on differences in the structure of the bacterial capsule. Different serotypes can cause infections ranging from mild to severe, depending on the characteristics of each strain. Although there are over 100 known serotypes, only a subset is responsible for most serious infections.3
How dangerous is pneumococcal disease for adults?
Severe cases of pneumococcal disease in adults can lead to death, neurological complications, hearing loss, developmental delays, or even limb loss.6